Green walnut fruit
Green walnut fruit
Green walnut is not just a workpiece for future delicious nucleoli. This is a whole world of hidden opportunities and an interesting biological process. Many, seeing a young, fragile fruit on a tree, simply do not notice anything special in it. But let's look at him more carefully.
Chemical composition and value
The immature fruit of a walnut is a storehouse of vitamins, minerals and other beneficial substances, although in a slightly different ratio than in a rheal. It contains many antioxidants that contribute to maintaining health. Of course, the taste of green nut is not as pleasant as that of ripe, but this does not diminish its nutritional value. It contains such necessary elements as magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, as well as B vitamins and K.
How to use?
Green nuts are not as easy to use as ripe. They can not simply be eaten: they will have to be carefully processed or used as part of other dishes. Often they are pickled, salt or fried. Such processing not only makes the taste more balanced, but also makes them safe for use. The green fruit is also used in traditional medicine. For example, in some countries, tinctures and decoctions are made from it to improve digestion or as a tonic. It is important to remember that it all depends on the conditions in which the nut is grown and how it is processed.
Why is the green nut still not ripe?
The reason why we do not eat green nuts just like that is in a high concentration of tannins. They give him a bitter and tart taste. Also, green nuts contain more water, and they are not as crispy and juicy as ripe. The maturation process is a complex biochemical transformation that leads to a gradual change in the chemical composition, giving the nut to the taste and texture. Therefore, until the fetus is ripening, it is not recommended, although there is a benefit from it. As a result, green nut, although not as popular as ripe, is an interesting and potentially useful product. You just need to know him, as well as cook.
AppropriateProducts
Corresponding products
The best soldproducts
The best -selling products-
 Washed fruits of walnut xin2
Washed fruits of walnut xin2 -
 Half of the nuclei of Yunnan walnuts of the lightest color
Half of the nuclei of Yunnan walnuts of the lightest color -
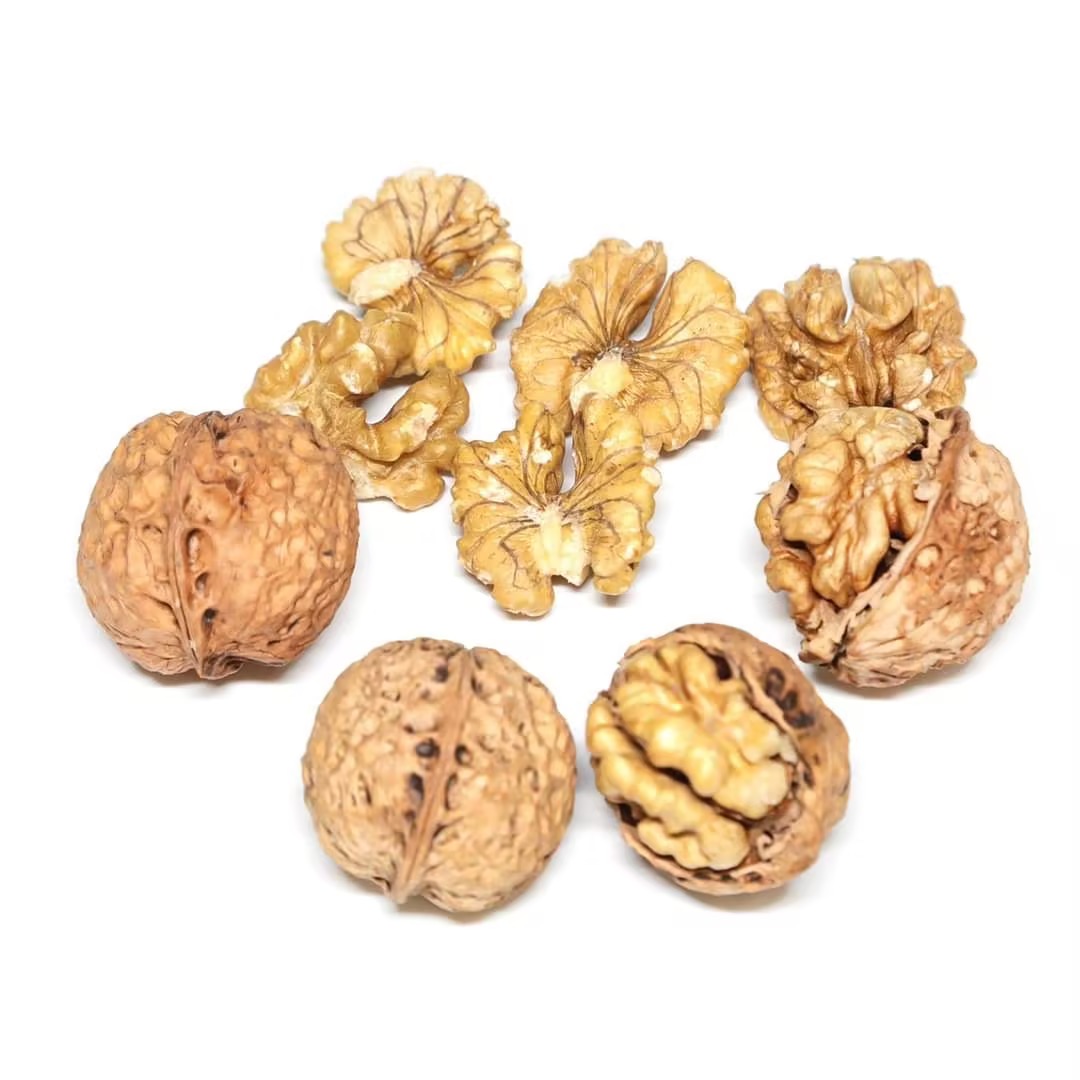 Washed fruits of Yunnan nut
Washed fruits of Yunnan nut -
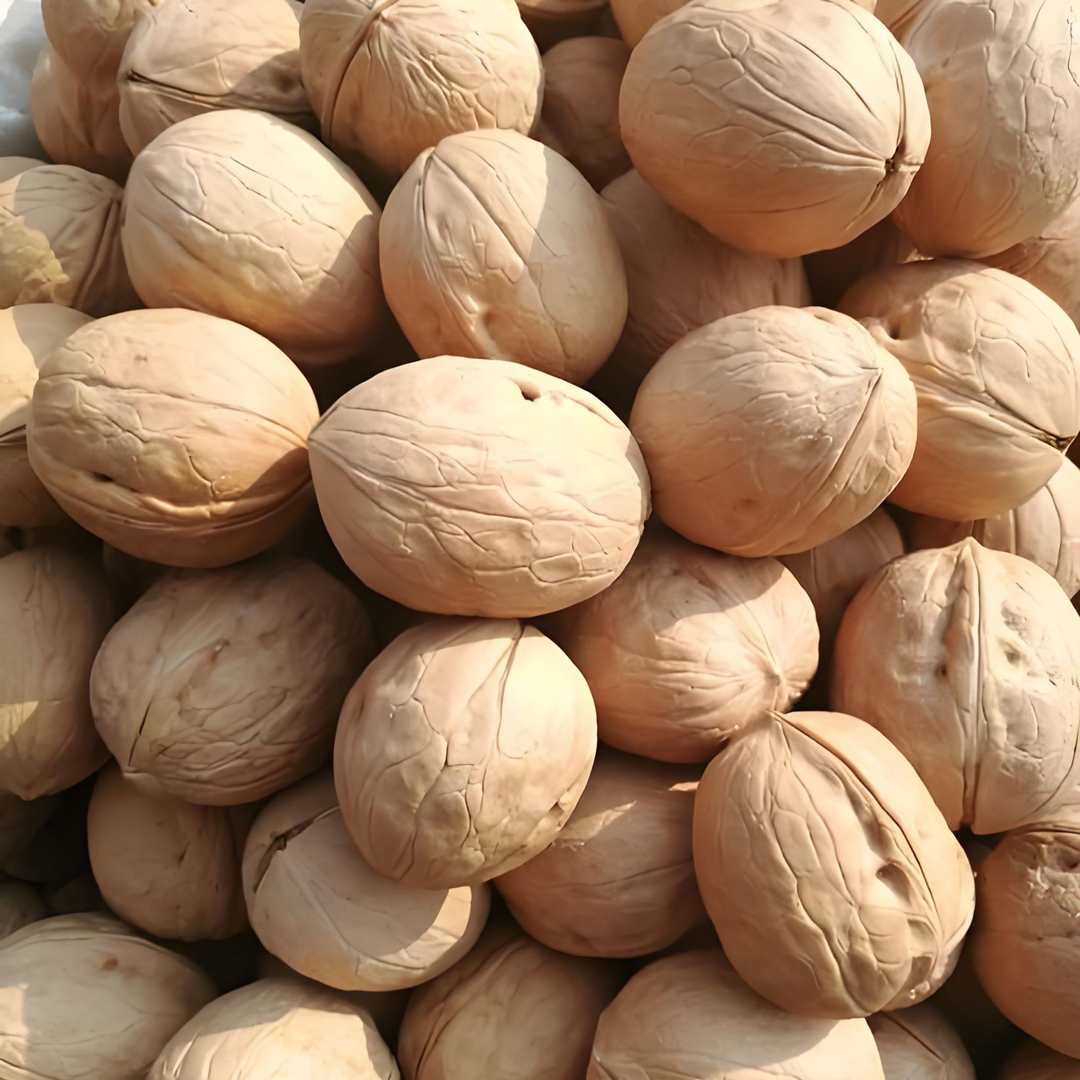 Washed fruits 33 walnuts
Washed fruits 33 walnuts -
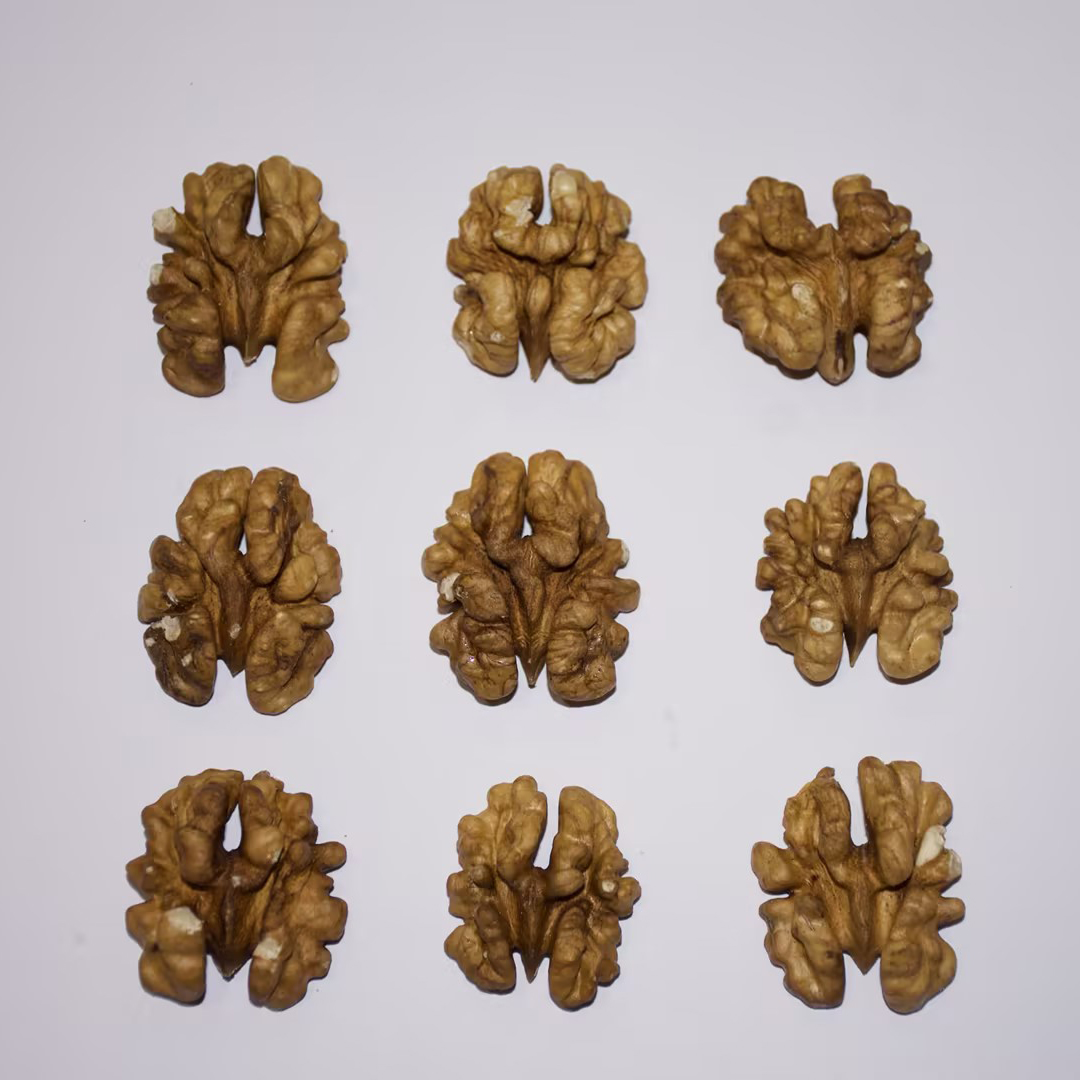 Half of the nuclei of walnut nucleus is a normal light color
Half of the nuclei of walnut nucleus is a normal light color -
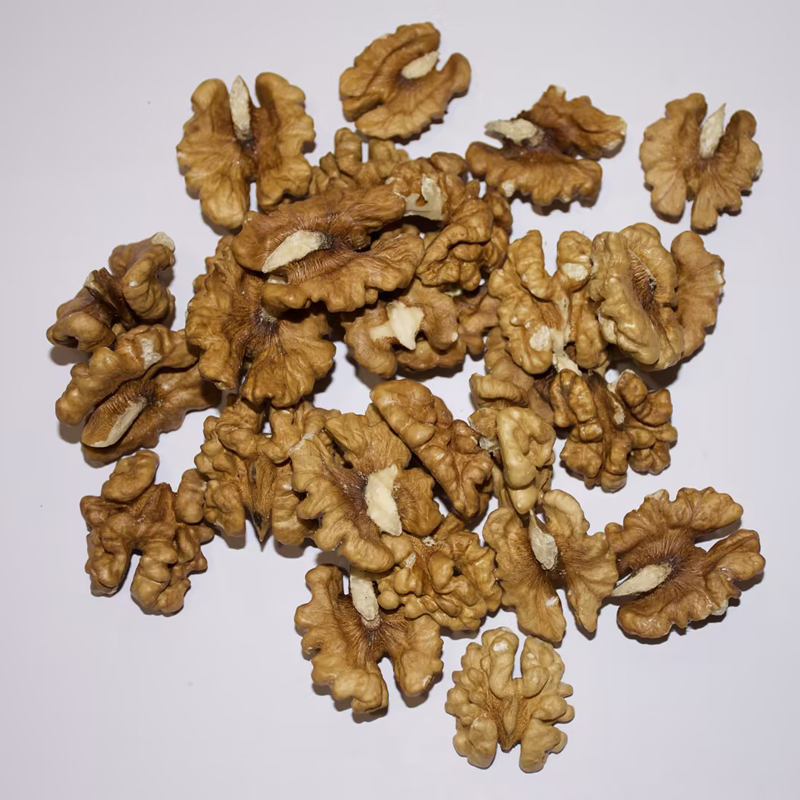 Normal light color of 185 halves of walnut nuclei
Normal light color of 185 halves of walnut nuclei -
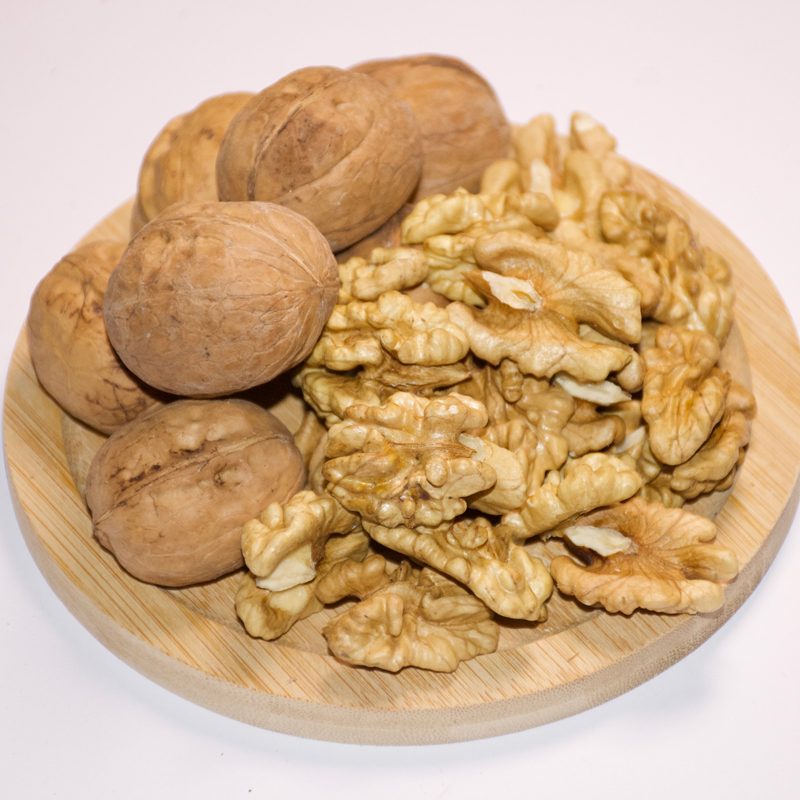 Half of the nuclei of walnuts of the lightest color Xin2
Half of the nuclei of walnuts of the lightest color Xin2 -
 Normal light Yunnan nut nuclei quarter
Normal light Yunnan nut nuclei quarter -
 White tetrahedral core of walnut
White tetrahedral core of walnut -
 Normal light color Xin2 of walnut nucleus the size of a quarter
Normal light color Xin2 of walnut nucleus the size of a quarter -
 Walnuted fruits of walnut xin2
Walnuted fruits of walnut xin2 -
 The nuclei of Yunnan walnuts of light color, mixed in half and quarters
The nuclei of Yunnan walnuts of light color, mixed in half and quarters
Connectedsearch
Related search- Manufacturers of sinji walnut nuclei
- Factories that produce photos of walnut fruits
- Cheap suppliers Yunnan head two paths
- Cheap 33 walnut fruit of suppliers
- Cheap Xinfen Gregs Suppliers
- Cheap price of purified walnuts for sale
- OEM Oulf Cake manufacturers
- Cheap for 100 g of calories of purified walnuts of factories
- Sinfan Jianbai Tou Road processing plant processing plant.
- Suppliers of walnuts